Understanding the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN)
The American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) plays a vital role in managing Internet resources, serving one of the most essential functions in modern digital infrastructure. Here we explore ARIN’s mission, services, and impact as a Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
In Short
- ARIN oversees the allocation of IP addresses and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) across the U.S., Canada, and parts of the Caribbean as one of five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs).
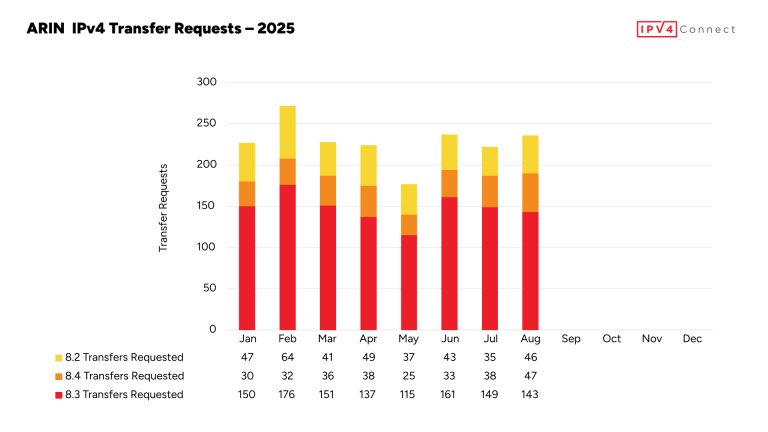
- Following IPv4 depletion in 2015, ARIN has implemented transfer policies and promotes IPv6 adoption while managing remaining IPv4 resources.
- Beyond allocation, ARIN offers critical services such as Whois database management, technical coordination, and educational initiatives to support the internet community.
What is ARIN?
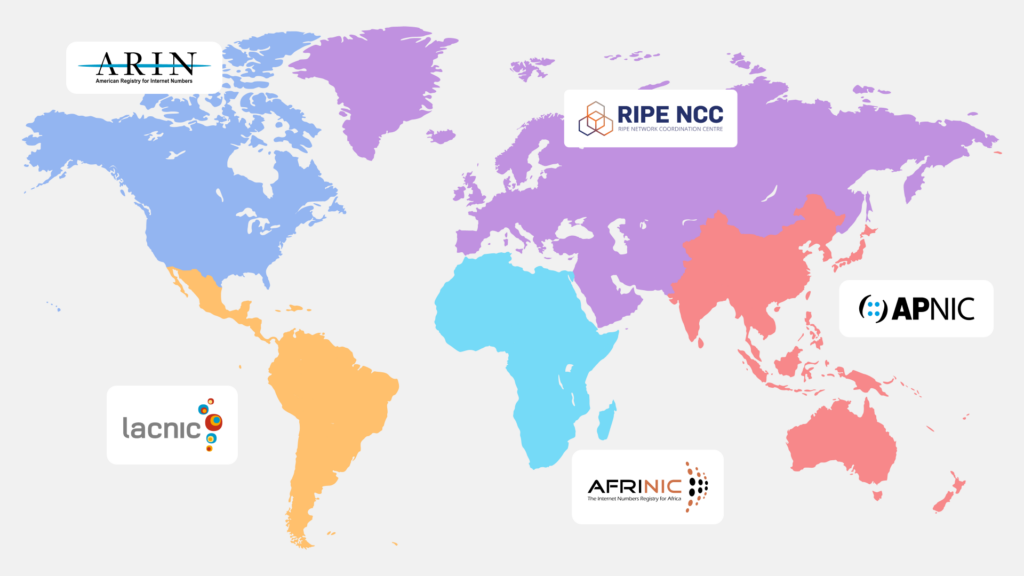
ARIN is one of five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) responsible for allocating and managing Internet resources. They are broken up into different regions:
- AFRINIC – Africa
- APNIC – Asia-Pacific
- ARIN – North America
- LACNIC – Latin America and Caribbean
- RIPE NCC – Europe, Central Asia, and the Middle East
These registries ensure the efficient and fair distribution of IP addresses and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) to maintain global Internet connectivity.
Geographic Scope of ARIN
ARIN’s jurisdiction covers a diverse range of territories, including:
- Canadian Sector: Canada
- Caribbean and North Atlantic Islands Sector: Approximately 20 island nations and territories, including Jamaica, the Bahamas, and St. Lucia
- Outlying Areas Sector: Remote territories such as St. Helena, Bouvet Island, Heard and McDonald Islands, and Antarctica
- United States Sector: The United States, Puerto Rico, US Minor Outlying Islands, and the Virgin Islands
Service Regions
ARIN’s jurisdiction covers four primary sectors:
- United States: Includes the mainland, Puerto Rico, and U.S. territories.
- Canada: Encompasses the entire country.
- Caribbean and North Atlantic Islands: Covers about 20 island nations and territories.
- Outlying Areas: Includes remote locations such as Antarctica.
Core Functions and Services of ARIN
Resource Management
ARIN manages the allocation of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, along with ASNs, across its service region. Since IPv4 exhaustion, it has enforced strict transfer policies and strongly advocates for IPv6 adoption to ensure fair and efficient resource distribution.
Registry and Database Services
ARIN maintains vital registry services, including:
- Whois Database: A public directory providing details on IP address assignments and routing information.
- WhoWas Database: A historical record of IP address ownership.
- Internet Routing Registry (IRR): Ensuring transparency and supporting network security.
Technical and Security Services
ARIN provides essential technical support, including:
- Reverse DNS Management for accurate domain resolution.
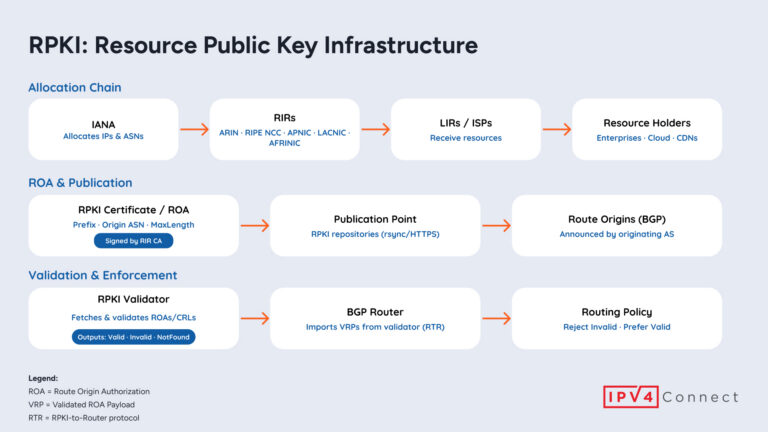
- Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) to enhance routing security.
- Collaboration with other RIRs to ensure seamless global resource coordination.
Policy Development and Community Support
ARIN collaborates with stakeholders to develop policies governing IP allocation and offers educational initiatives for Internet governance.
Focus Areas
ARIN prioritizes internet stability, security, and transparency within its jurisdiction. Key initiatives include:
- Routing Security: Strengthening the integrity of internet routing through RPKI.
- Community Education: Offering technical training and educational programs to enhance understanding of network management and security.
- Internet Governance: Actively participating in policy discussions to shape the future of internet resource management.
- IPv4 & IPv6 Transition: Facilitating the transfer and efficient use of remaining IPv4 addresses while encouraging IPv6 adoption.
IPv4 and IPv6 Management
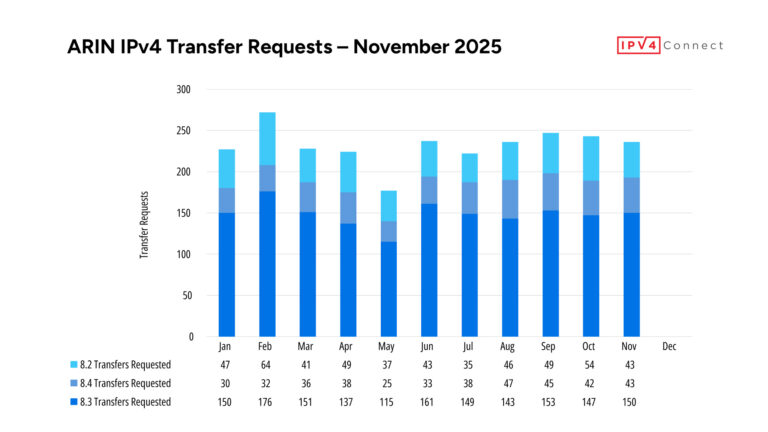
Since declaring IPv4 exhaustion in 2015, ARIN has focused on managing existing resources efficiently. It offers a waiting list for reclaimed IPv4 addresses and supports an active transfer market to meet ongoing demand. Meanwhile, the organization continues to advocate for the adoption of IPv6 to ensure long-term internet growth.
ARIN Registration Services
The American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) provides authoritative and comprehensive registration services, including the allocation, assignment, and transfer of essential internet number resources:
- IPv4 addresses
- IPv6 addresses
- Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs)
ARIN’s role in managing the registration of IP addresses and ASNs within its service region is conducted with a high level of professionalism and dedication to serving the community’s diverse needs. This ensures a structured and efficient oversight of internet number resource distribution, essential for maintaining the robustness and reliability of global internet infrastructure.History and Evolution of ARINThe need for structured IP management emerged in the 1990s, leading to the establishment of ARIN in 1997. Since then, ARIN has played a crucial role in Internet governance, evolving alongside technological advancements:
- 2002-2005 – ARIN’s jurisdiction was refined with the creation of LACNIC and AFRINIC.
- 2015 – ARIN announced the depletion of its IPv4 address pool, marking a major shift toward IPv6 adoption.
The Future of ARIN
With the depletion of IPv4, ARIN actively promotes IPv6 adoption and manages resource transfers to ensure sustainability. Through its technical services, registry management, and policy leadership, ARIN continues to be an essential pillar of Internet stability and security.
Conclusion
ARIN is a cornerstone of internet infrastructure, serving far beyond an IP address registry. It functions as an essential governing body of the internet. Through its services, transparent policies, and active community engagement, ARIN ensures the stable and secure evolution of the internet.For ISPs, network operators, and organizations reliant on internet resources, understanding ARIN’s role is key. As the internet continues to evolve, ARIN’s resource management and regional development makes it crucial in shaping future connectivity.