Reverse DNS: Everything You Need to Know
Reverse DNS (RDNS) maps IP addresses to hostnames using PTR records. Learn how reverse DNS works, and how ARIN manages delegations
Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) manage and distribute IP address allocations and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) within specific geographic regions. They ensure fair distribution, maintain database accuracy, and support internet infrastructure growth. The five RIRs—ARIN, RIPE NCC, APNIC, LACNIC, and AFRINIC—coordinate with IANA to maintain global IP address management.

Reverse DNS (RDNS) maps IP addresses to hostnames using PTR records. Learn how reverse DNS works, and how ARIN manages delegations

ARIN increases annual fees by 5% for 2026, maintains fee cap, and extends IPv6 waiver for 3X-Small organizations.

IANA, The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, manages global IP addresses, DNS root zones, and protocols, ensuring internet stability
APNIC manages IP address distribution in the Asia-Pacific, supports IPv6 adoption, enhances internet security, and provides registry services
IPv4 addresses are essential for internet communication, but limited availability is pushing the transition to IPv6 for future connectivity.
AFRINIC manages IP addresses and ASNs across Africa, promoting IPv4 and IPv6 adoption and providing services for internet stability.

The hidden dangers of IP transfer abuse. How cybercriminals use IP addresses for malicious activities like spam, phishing, and malware.
ARIN manages IP addresses and ASNs across North America, promoting IPv6 adoption and providing essential services for internet stability.
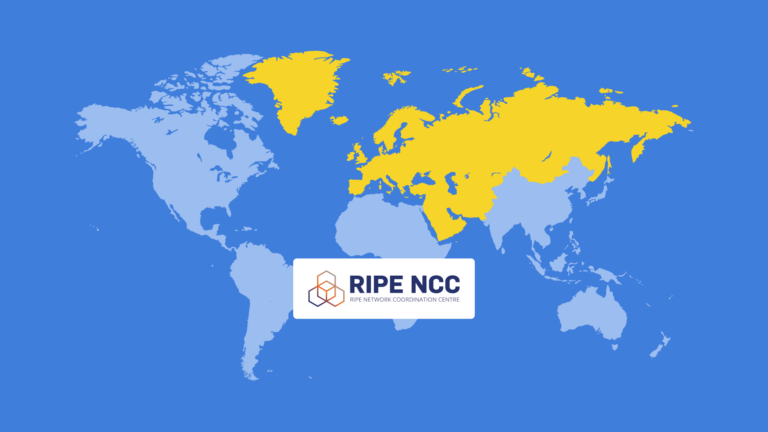
RIPE NCC is the original Regional Internet Registry, that assigns IP addresses for 76 countries in Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia.
Email me when new IPv4 inventory matches my criteria.
Error: Block data unavailable.
You’ll now receive email alerts when new IPv4 inventory matches your preferences.
Are you absolutely sure you want to delete your account? This action cannot be undone.