Reverse DNS: Everything You Need to Know
Reverse DNS (RDNS) maps IP addresses to hostnames using PTR records. Learn how reverse DNS works, and how ARIN manages delegations
This is our IPv4 knowledgebase, covering the basics of networking. It includes essential terms and concepts in IP addressing, subnetting, routing, NAT, CIDR, ARP, and DNS.

Reverse DNS (RDNS) maps IP addresses to hostnames using PTR records. Learn how reverse DNS works, and how ARIN manages delegations
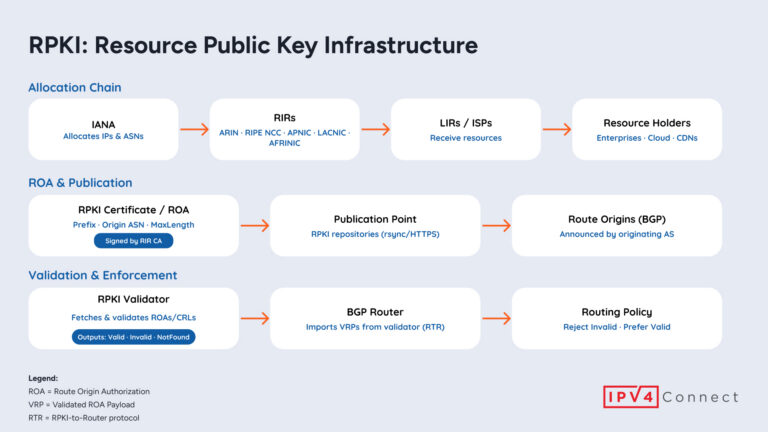
RPKI adds cryptographic trust to BGP, preventing hijacks and leaks. Learn how ROAs, validators, and routers keep routing secure.

ICANN is a non-profit, private, and international organization responsible for maintaining and coordinating the unique identifiers essential for the global internet

Telecom companies face rising cyber threats and espionage, requiring cybersecurity strategies to protect infrastructure, data, and reputation

Key Differences between MAP-T vs. CGNAT: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Choosing the Right IPv4-to-IPv6 Transition Solution

Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol that secures internet communications between servers, browsers, and applications.

IANA, The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, manages global IP addresses, DNS root zones, and protocols, ensuring internet stability
APNIC manages IP address distribution in the Asia-Pacific, supports IPv6 adoption, enhances internet security, and provides registry services
IPv4 addresses are essential for internet communication, but limited availability is pushing the transition to IPv6 for future connectivity.
AFRINIC manages IP addresses and ASNs across Africa, promoting IPv4 and IPv6 adoption and providing services for internet stability.
Email me when new IPv4 inventory matches my criteria.
Error: Block data unavailable.
You’ll now receive email alerts when new IPv4 inventory matches your preferences.
Are you absolutely sure you want to delete your account? This action cannot be undone.