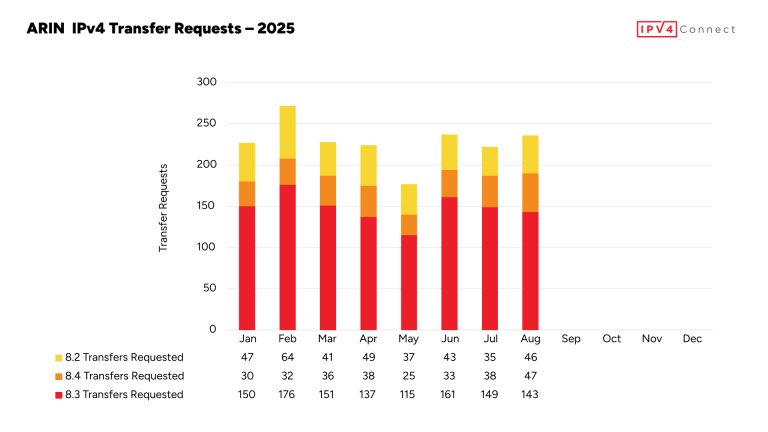
APNIC: The Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre
The Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) plays a crucial role in managing internet resources across the Asia-Pacific region, ensuring the efficient allocation of IP addresses and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs). This article explores APNIC’s mission, services, and its impact as a Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
In Short
- APNIC facilitates the allocation of IP addresses and ASNs in the Asia-Pacific region as one of five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs).
- Following IPv4 depletion, APNIC has implemented transfer policies and promotes IPv6 adoption while managing the remaining IPv4 resources.
- Beyond resource allocation, APNIC provides critical services, including Whois database management, technical coordination, and educational initiatives to support the internet community.
- APNIC offers essential services, including Whois database management, network security, and educational initiatives for the internet community.
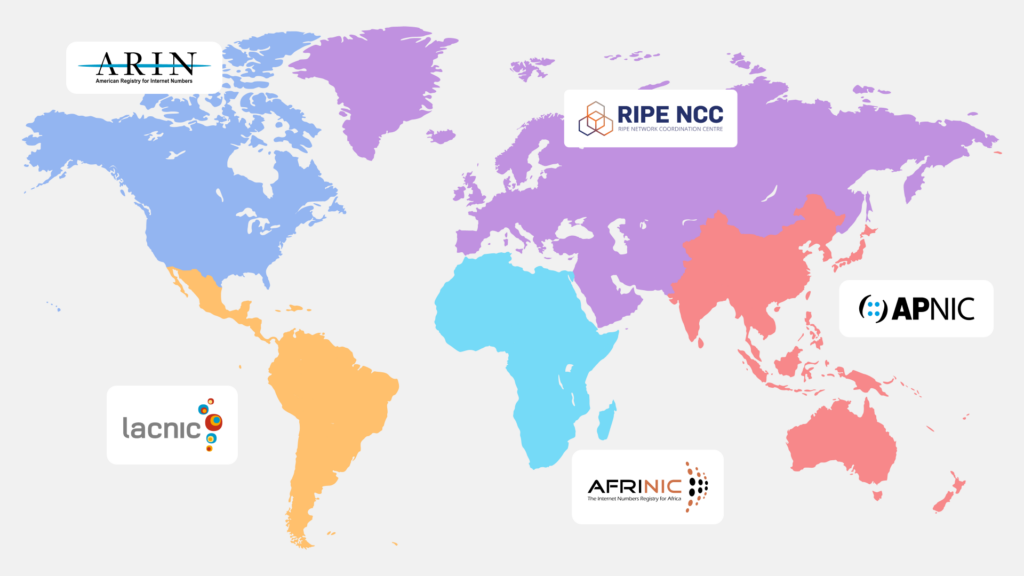
The Five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs)
Five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) are responsible for managing and distributing internet resources:
- AFRINIC – Serving Africa
- APNIC – Overseeing Asia-Pacific
- ARIN – Managing North America
- LACNIC – Covering Latin America and the Caribbean
- RIPE NCC – Supporting Europe, Central Asia, and the Middle East
These registries ensure equitable distribution of IP addresses and ASNs to maintain seamless global connectivity.
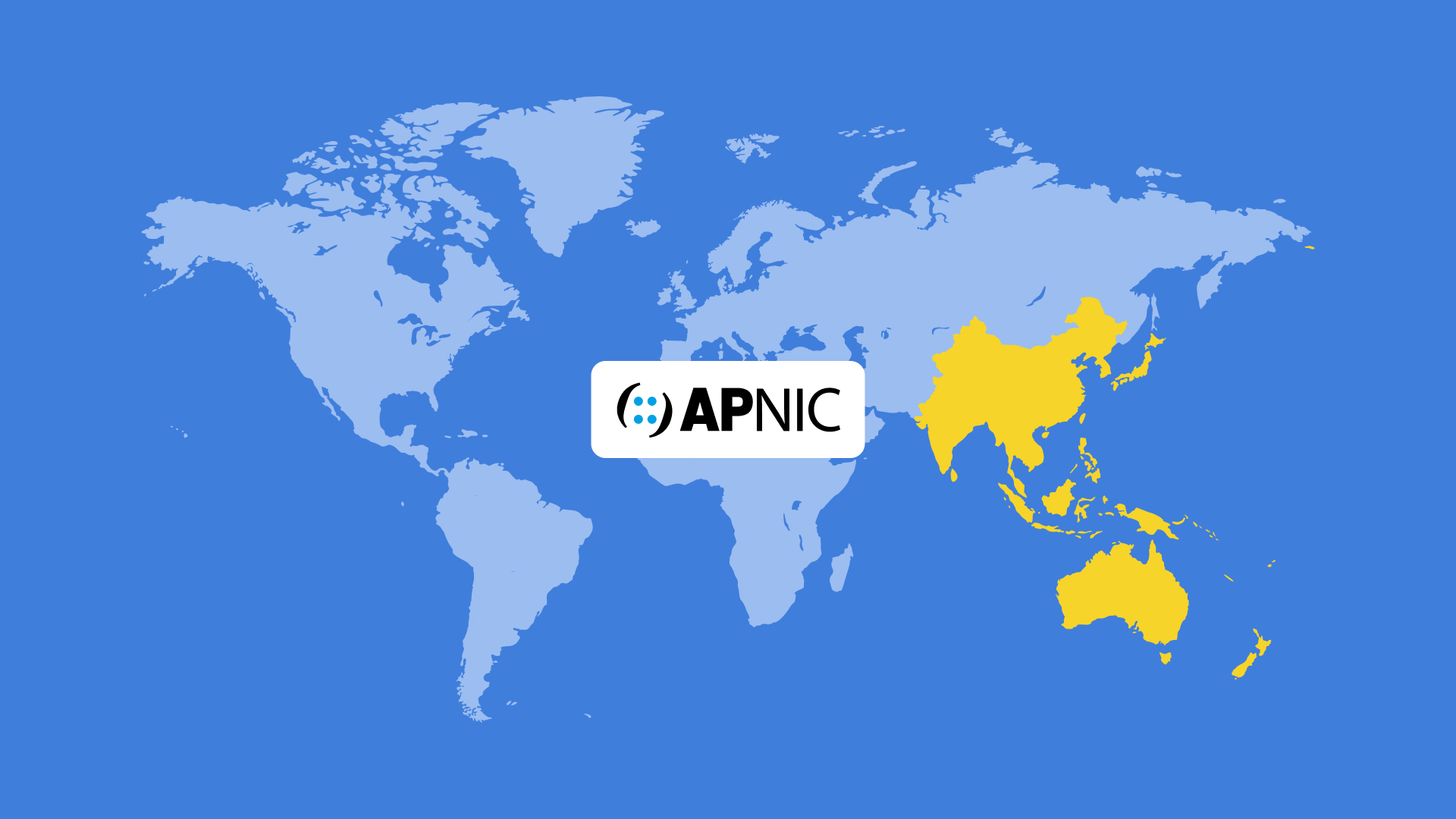
Geographic Coverage
APNIC operates across a vast region, including:
- East Asia: Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Mongolia
- Southeast Asia: Including Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos, Brunei, and Timor-Leste
- South Asia: Serving India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and the Maldives
- Oceania: Covering Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, and various Pacific Islands
Core Functions and Services
Internet Resource Management
APNIC oversees the allocation of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, along with ASNs, across its service region. To address IPv4 exhaustion, APNIC enforces strict transfer policies and promotes IPv6 adoption for sustainable internet expansion.
Registry and Database Services
APNIC maintains vital registry services, including:
- Whois Database: A public directory for IP address assignments and routing details.
- WhoWas Database: Maintaining historical records of IP ownership.
- Internet Routing Registry (IRR): Enhancing network transparency and security.
Technical and Security Services
APNIC delivers vital technical services, including:
- Reverse DNS Management to improve domain resolution.
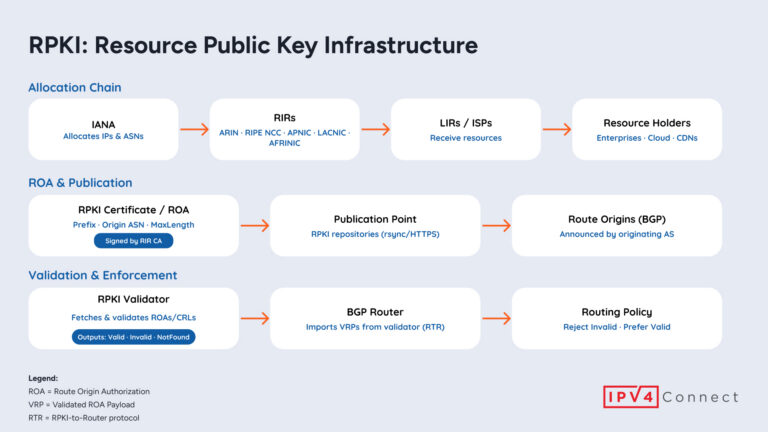
- Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) to strengthen routing security and prevent network hijacking.
- Global RIR Collaboration to ensure seamless coordination of internet resources.
Policy and Community Development
As an RIR, it works alongside industry stakeholders to develop policies governing IP resource distribution and fosters knowledge-sharing through various initiatives.
Strategic Priorities
APNIC emphasizes security, efficiency, and transparency in internet governance. Key focus areas include:
- Routing Security: Strengthening global routing protocols through RPKI implementation.
- Education and Training: Conducting workshops and technical training to support network operators.
- Internet Governance: Engaging in global policy-making to influence the future of internet resource allocation.
- IPv4 & IPv6 Transition: Supporting IPv6 adoption while managing IPv4 resource transfers.
Managing IPv4 and IPv6 Resources
Since IPv4 depletion, APNIC has implemented strict resource management strategies, including waitlists for IPv4 allocations and facilitating transfers. It also actively promotes IPv6 adoption to ensure long-term internet sustainability.
Registration Services
APNIC provides internet resource registration services, including:
- IPv4 Address Allocation
- IPv6 Address Distribution
- ASN Assignments
By ensuring efficient internet resource oversight, it plays a pivotal role in maintaining the reliability of global connectivity.
APNIC’s Evolution and History
To meet the rising demand for structured IP management, APNIC was established in 1993. Its milestones include:
- 2002-2005: Refining jurisdiction as LACNIC and AFRINIC were formed.
- 2011: Becoming the first RIR to deplete its IPv4 address pool.
- 2015-Present: Driving IPv6 adoption and refining IP transfer processes for sustainable growth.
The Future
As IPv4 addresses become scarcer, APNIC remains focused on IPv6 adoption and refining resource distribution policies. By far the largest Regional Internet Registry by population and land mass, and with China and India as members, it is incredibly influential. Its technical expertise, policy leadership, and active community engagement, it continues to shape the Asia-Pacific – and global – internet landscape.
Conclusion
APNIC is more than an internet registry—it is central to internet governance in the Asia-Pacific region. By implementing transparent policies, delivering essential services, and engaging with the community, it ensures the internet’s continued growth and security. For ISPs, network providers, and businesses relying on internet resources, understanding the five Regional Internet Registries’ roles is essential for long-term connectivity planning.