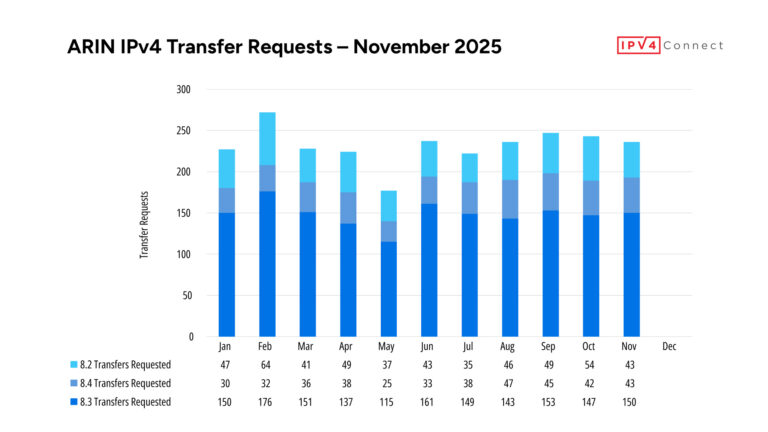
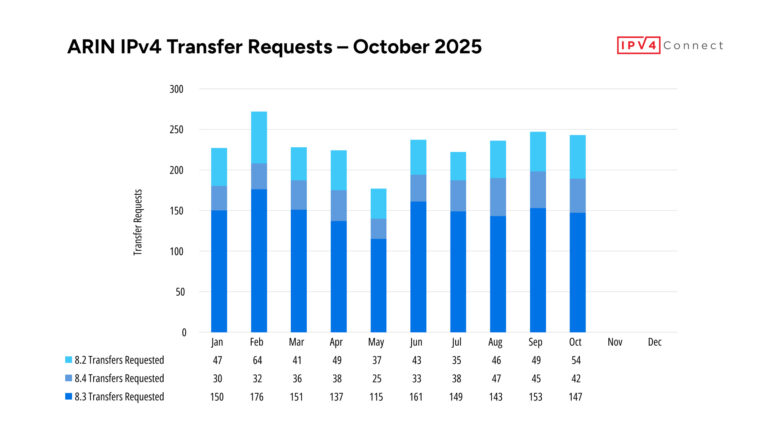
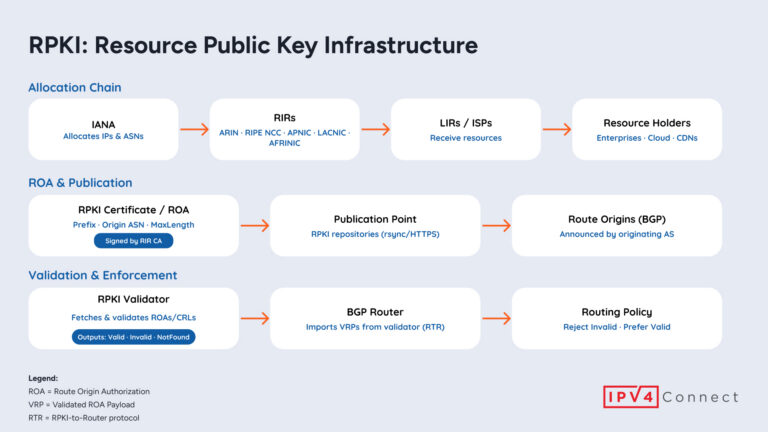
The Basics
IP2 Location is a geolocation database and software solution1 that determines the physical location of an IP address. It is commonly used by businesses for targeted marketing, fraud prevention, content personalization, and security applications.
The service works by referencing an IP address database that links IP addresses to geographic information, and can identify the geographic location of users, such as country, region, city, and even the precise latitude and longitude of an IP address. Additionally, IP2 Location detects IP addresses associated with anonymous proxies, VPNs, and other privacy tools.

How IP2Location Works
Every device connected to the internet has an IP (Internet Protocol) address. This works as a digital fingerprint, uniquely identifying a device among millions of others. IP2Location takes an IP address and references it against other available data, to provide information about the IP; country, region, city, latitude, longitude, and sometimes even ZIP codes.
What Data Does It Capture?
As the name implies, the IP2Location focuses primarily on geolocation data. The company characterizes this as as non-intrusive “coarse” information, and retrieves the data without explicit user consent
- Country, Region, and City: The physical location of the IP address.
- ZIP Code
- Area Code
- Elevation
- ISP (Internet Service Provider): The company providing internet access for the IP.
- Domain Name: The domain associated with the IP address.
- Time Zone and Coordinates: Precise latitude and longitude data.
- Connection Type: Identifies if the connection is DSL, broadband, etc.
- ASN & District
- Weather Station Data
- Address Type & Usage Type
- Time Zone, ISP, Domain, Net Speed
- Advertising Category
- Mobile Carrier Information, MNC, MCC
- Anonymous Proxies: Detects IP addresses associated with proxies, VPNs, or other anonymizing tools.
IP Address is a Fingerprint
Every device connected to the internet has an IP (Internet Protocol) address. Think of it as a digital fingerprint, a unique string of numbers identifying a device in the vast web of connectivity. IP 2Location takes this identifier and translates it into meaningful data: country, region, city, latitude, longitude, and sometimes even ZIP codes. It’s a process of transforming abstract numbers into tangible context.
But how does this work? The technology relies on multiple databases, continuously updated, that link IP ranges with physical locations. It’s an ongoing process of aggregating data from various sources, including regional internet registries and network providers.
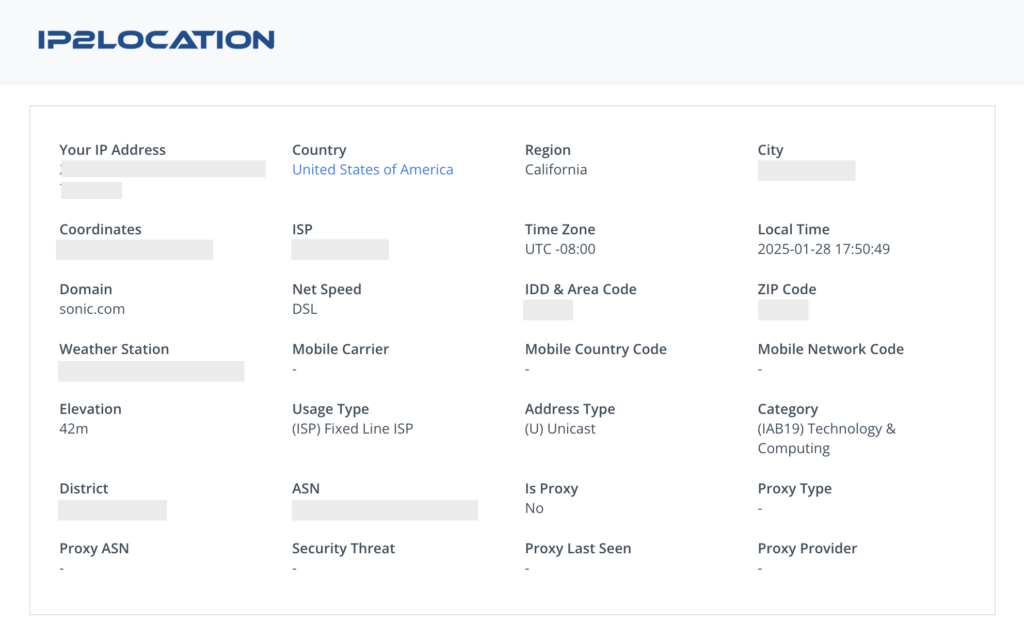
Use Cases for IP2 Location
IP2Location’s applications span several industries, from marketers, to security professionals and developers. Here are a few scenarios where IP2Location proves its worth:
- Targeted Advertising: Digital marketers use IP2Location to geotarget ads for local businesses based on a user’s location.
- Content Localization: Streaming services like Netflix use IP2Location to manage content restrictions. Your geographical can determine whether distribution rights on shows and movies available to you, ensuring legal compliance.
- Fraud Prevention: E-commerce platforms use IP2Location to verify the legitimacy of transactions. Flagging transactions on credit cards from other geographic regions is a key use case.
- Cybersecurity: IP2Location helps track and mitigate cyber threats by identifying the geographic origins of malicious traffic. Security teams can block regions associated with high levels of cyberattacks.
- Web Analytics: Website owners analyze visitor data with IP2Location to understand their audience better. Knowing where your traffic comes from can shape content strategies and business decisions.

Ethics & Privacy Concerns with Geolocation
IP2Location’s use of geolocation data poses questions about ethics and privacy. The use of geolocation can verge on surveillance. IP2Locatiom itself frames this as providing efficiency and security, not undermining privacy.2 The company limits the level of identifying detail of information it provides for this reason.
And some of this depends on implementation. Organizations that use IP2Location also need to respect the privacy of users. Transparent data policies, informed consent, and adherence to regulations like the GDPR are essential safeguards.
Limits of Geolocation
It’s worth noting that IP2Location isn’t foolproof. The accuracy of IP-based geolocation3 depends on various factors, including the type of IP address (static or dynamic) and the location of the ISP. While city-level precision is often achievable, pinpointing a user’s exact location is rare.
Misconceptions about the technology’s capabilities can lead to misplaced trust. IP2Location can tell you where an IP address is likely originating, but it cannot identify a specific user or device. The difference between probabilistic data and personal data is significant, and conflating the two can lead to flawed conclusions.
Geolocation is Here to Stay
As the internet evolves, so too do geolocation technologies like IP2Location. The rise of IPv6, the next-generation internet protocol, introduces new challenges and opportunities. With trillions of possible addresses, the scope for IP2Location to refine its algorithms and expand its database is immense.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence will also play a role. Predictive analytics could enhance IP2Location’s accuracy, integrating it seamlessly into broader data ecosystems. As IoT (Internet of Things) devices proliferate, geolocation will become even more crucial for managing and securing our interconnected world.
The Takeaway
IP2 Location is widely used, and shapes the way we interact with digital spaces. It bridges the gap between the virtual and the physical, making the internet a little less abstract and anonymous. From personalized ads to cybersecurity, its influence is as wide-ranging as the web itself.
Yet, like all tools, its value lies in how it’s used. As geolocation is integrated into almost everything internet, it is important to consider that technology as a tool works best when it respects the boundaries of ethics and privacy. In an age where every click leaves a trace, it is useful to understand how tools like IP2 Location work.
- Understanding Geofeeds & Updating Geolocation (Brander Group) ↩︎
- Privacy Policy: IP2 location ↩︎
- How to Update Your IPv4 Geolocation (Brander Group) ↩︎